
- WIRESHARK HTTPS HOST PRO
- WIRESHARK HTTPS HOST SOFTWARE
- WIRESHARK HTTPS HOST PASSWORD
- WIRESHARK HTTPS HOST MAC
This file can subsequently be configured in Wireshark ( #Using the (Pre)-Master Secret). To be precise, their underlying library (NSS, OpenSSL or boringssl) writes the required per-session secrets to a file. The key log file is a text file generated by applications such as Firefox, Chrome and curl when the SSLKEYLOGFILE environment variable is set. The RSA private key only works in a limited number of cases.
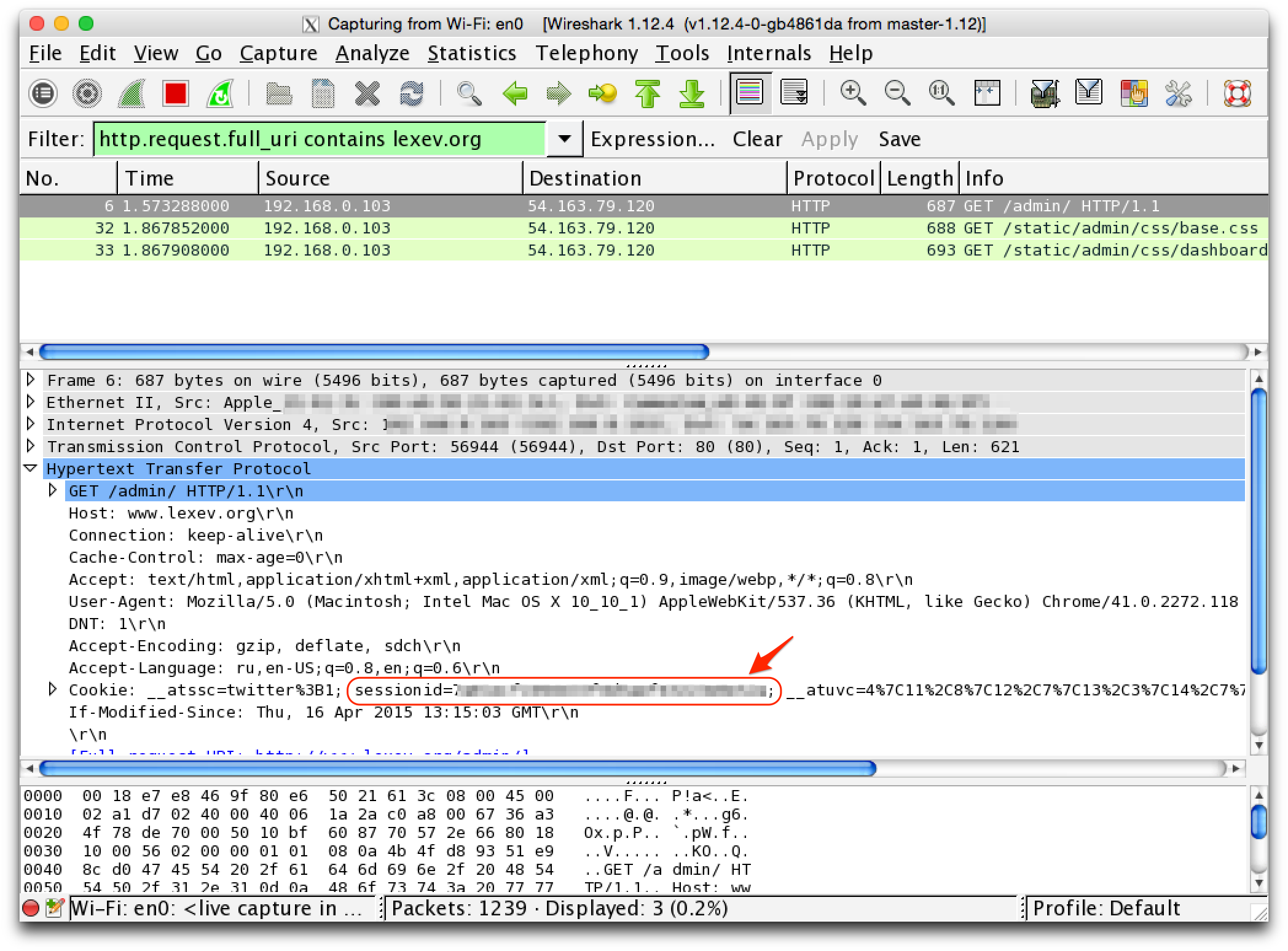
Key log file using per-session secrets ( #Usingthe (Pre)-Master Secret).Ī key log file is a universal mechanism that always enables decryption, even if a Diffie-Hellman (DH) key exchange is in use. Wireshark supports TLS decryption when appropriate secrets are provided. Use of the ssl display filter will emit a warning. Since Wireshark 3.0, the TLS dissector has been renamed from SSL to TLS. The TLS dissector is fully functional and even supports advanced features such as decryption of TLS if appropriate secrets are provided ( #TLS_Decryption).
WIRESHARK HTTPS HOST SOFTWARE
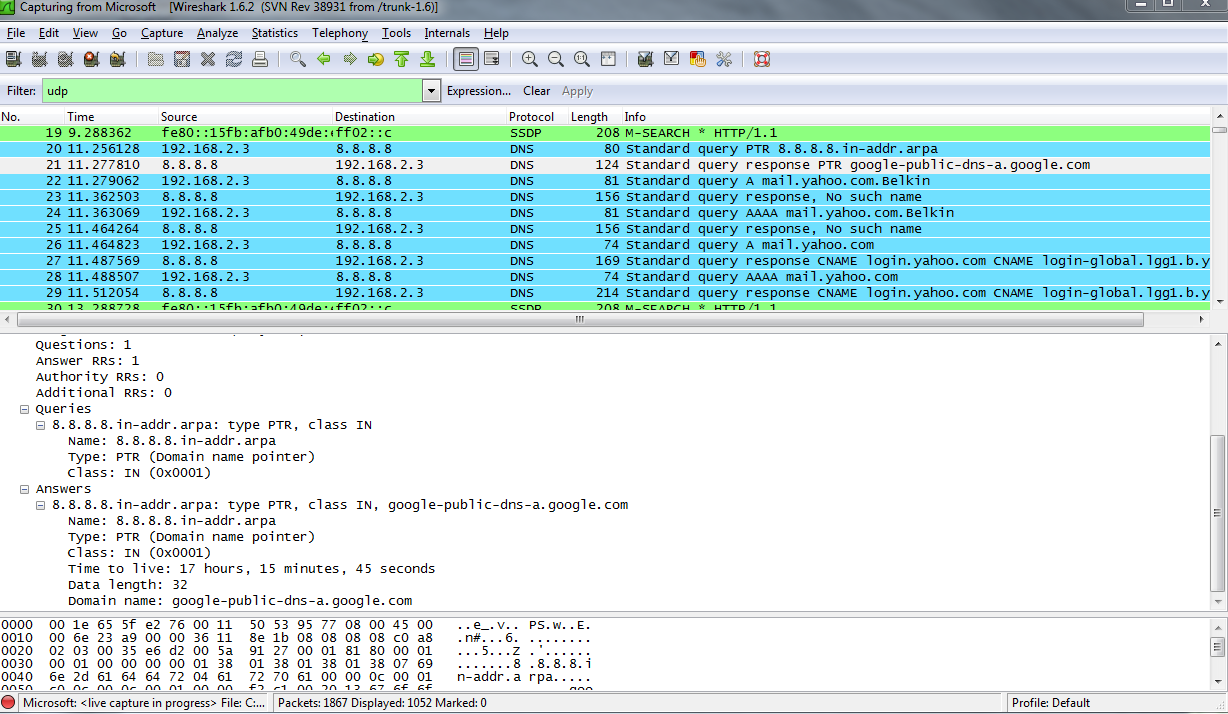
When a single port directly uses the TLS protocol, it is often referred to as SSL.įor historical reasons, software (Wireshark included) refer to SSL or SSL/TLS while it actually means the TLS protocol since that is nowadays what everyone uses. To change from unencrypted to encrypted, (START)TLS is used. Some applications (such as email) use a single port for both unencrypted and encrypted sessions. X.509 certificates for authentication are sometimes also called SSL Certificates. These names are often used interchangeably which can lead to some confusion:Ī configuration that uses the SSL protocol (SSLv2/SSLv3) is insecure. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is the predecessor of the TLS protocol. It is used most commonly in web browsers, but can be used with any protocol that uses TCP as the transport layer. It provides integrity, authentication and confidentiality. Transport Layer Security (TLS) provides security in the communication between two hosts. Embedding decryption secrets in a pcapng file.That's why you're not seeing your Mac's traffic on the Internet from the virtual machine - the only machine whose Internet traffic you'll see is the virtual machine itself. If you want to capture wireless traffic on the virtual machine, you'll probably need to get a USB wireless adapter, plug it into your Mac, and have the virtual machine software give the adapter to the virtual machine rather than to the Mac. Your virtual machine probably has no wireless adapters it has only an "Ethernet adapter" which allows it to send packets to, and receive packets from, the host machine on which the VM software is running. The other thing to not that even though I want to sniff my wireless network, the only capture options with visible traffic are "eth0" and "any".

WIRESHARK HTTPS HOST MAC
See the Wireshark Wiki's "How to decrypt 802.11" page for more information.Īlternatively, if you only want the traffic between your Mac and other machines, you could capture with monitor mode turned off the traffic will not be encrypted at the LAN layer, but you won't see any other machines on the network unless they're sending your Mac packets or receiving packets from your Mac.
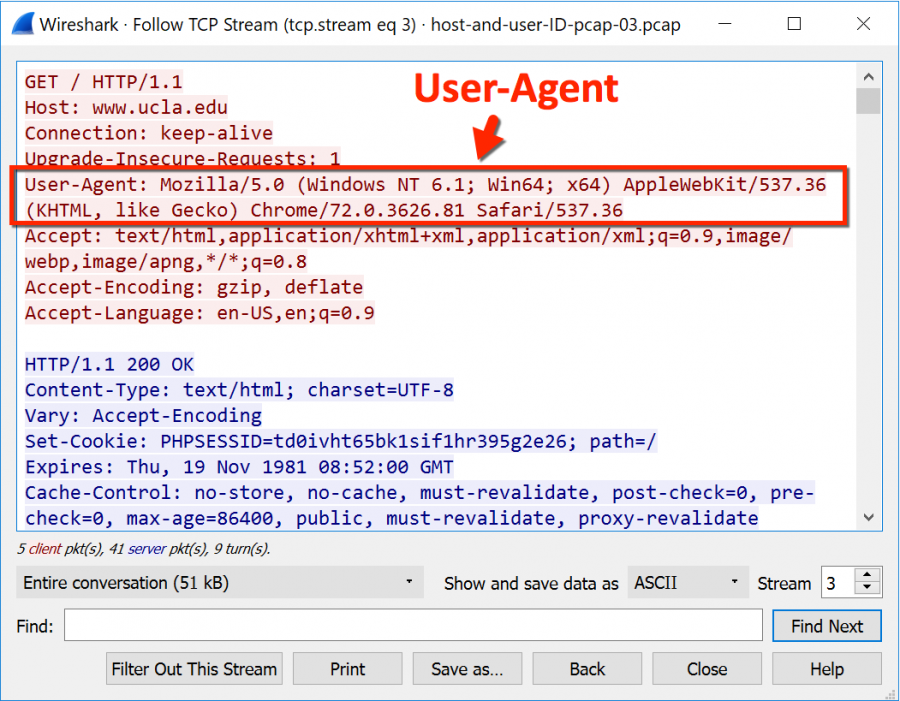
WIRESHARK HTTPS HOST PASSWORD
You'd have to tell Wireshark the password for your network to decrypt the packets, and, if the network uses WPA/WPA2 rather than WEP (which it probably does), you'd have to make sure you capture the initial "EAPOL handshake" for each machine on the network whose traffic you want to see. That's because you're capturing in monitor mode, and you're on a "protected" network using encryption, so the packets that Wireshark gets are encrypted.
WIRESHARK HTTPS HOST PRO
I first just downloaded Wireshark on my MacBook Pro with IOS Sierra and it only showed 802.1.1 interactions and all the protocols are 802.1.1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
